-

Manual Therapy
Joint Mobilization/Manipulation involves skilled manual therapy techniques where therapists apply precise, passive movements to joints within their natural range of motion. This targeted approach reduces pain, enhances joint mobility, and accelerates the restoration of optimal function, empowering patients to move freely and confidently.
Soft Tissue Mobilization: Hands-on therapy targeting muscles, ligaments, and fascia to break down scar tissue, improve blood flow, and decrease muscle tension.
Myofascial Release: Focused pressure and stretching applied to the fascial system to release restrictions, alleviate pain, and enhance tissue flexibility.
Muscle Energy Technique: Patient-active isometric contractions against a therapist's resistance designed to relax tight muscles, lengthen shortened tissues, and improve joint mobility.
-
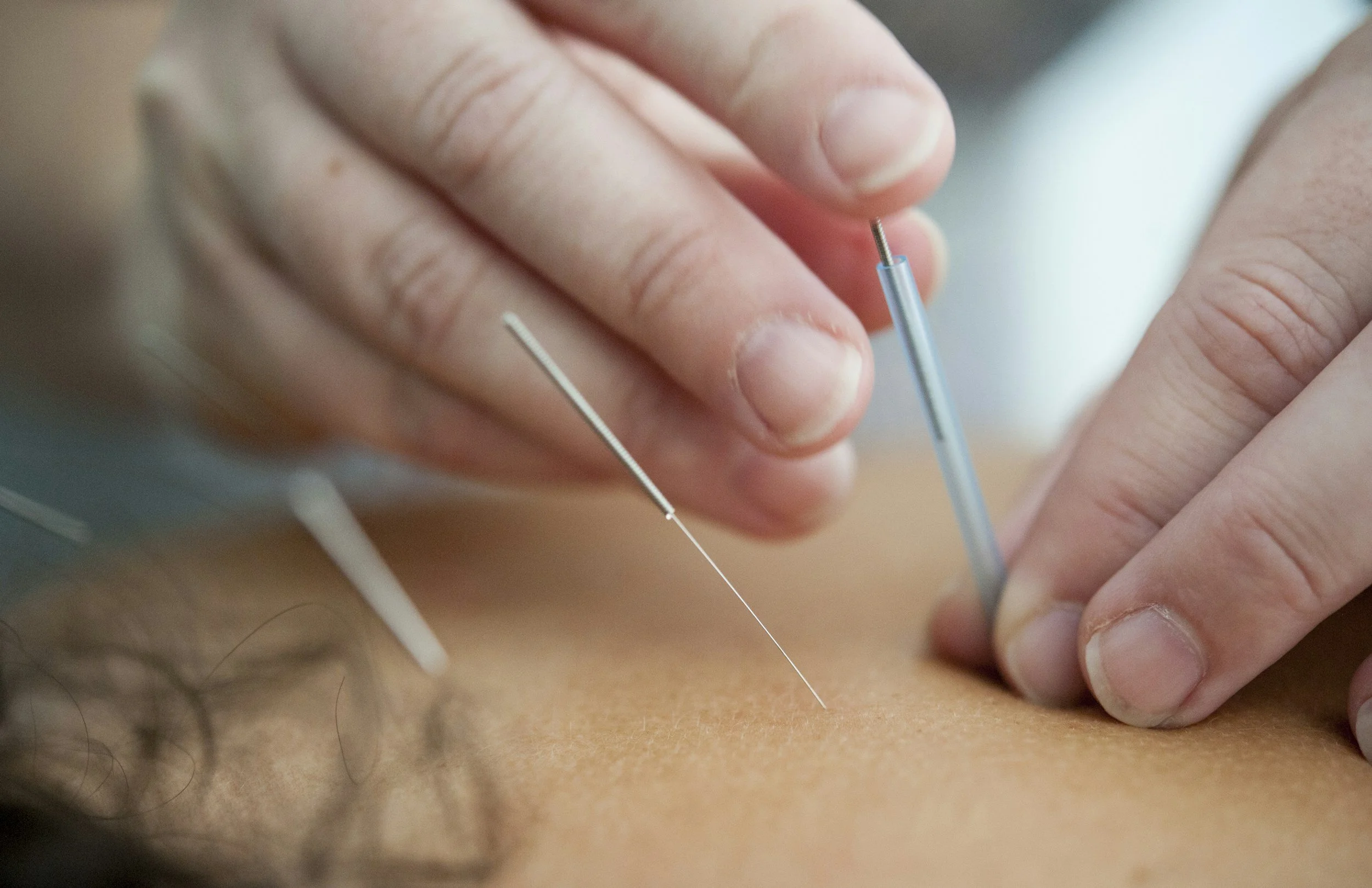
Dry needling
Dry needling targets trigger points within muscles and connective tissue to relieve soft tissue tension. By inserting fine needles into these tight spots, it disrupts muscle knots, improves blood flow, and normalizes nerve signaling. This process helps reduce inflammation by promoting the body’s natural healing response. Dry needling effectively restores movement and eases discomfort by addressing the underlying muscular and neurological dysfunction.
-
PELVIC HEALTH
Pelvic floor therapy focuses on strengthening and rehabilitating the muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that support the bladder, uterus, rectum, and other pelvic organs. These muscles play a crucial role in bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and core stability.
For both men and women, pelvic floor therapy treats conditions such as incontinence—both urinary and fecal—by retraining the muscles to improve control and reduce leakage. Pelvic pain, often caused by muscle tightness, nerve irritation, or injury, is addressed through targeted manual therapy, stretching, and relaxation techniques.
In pregnancy, pelvic floor therapy prepares the muscles to handle the increased load and stress, reducing discomfort and preventing future dysfunction. Postpartum, therapy helps restore muscle tone and function, supports recovery from childbirth injuries, and alleviates symptoms like pelvic pain or urinary incontinence.
Treatment typically includes individualized exercises (like Kegels), biofeedback, manual therapy, education on body mechanics, and lifestyle modifications. The goal is to restore optimal pelvic floor function, improve quality of life, and empower patients with the tools they need for ongoing pelvic health.
-

THERAPUETIC EXERCISE
Therapeutic exercise in physical therapy involves systematically planned movements designed to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the body. It targets specific muscles and joints to reduce pain, prevent injury, and improve overall mobility, enabling patients to regain independence and enhance quality of life.
-

Therapeutic activity
Therapy with a physical therapist focuses on the exact movements you use in daily life and sports. By practicing sport drills, walking, jogging, and household tasks, therapy helps you recover and move better. This approach builds strength, coordination, and stamina where you need it most, helping you safely return to your activities faster.
-

Neuromuscular Reeducation
Physical therapists use neuromuscular reeducation and balance training to help you move better and coordinate your body. These exercises retrain your nerves and muscles to respond correctly and stay stable during movement. This improves your body awareness, lowers fall risk, speeds up injury recovery, and boosts overall function. By fixing muscle imbalances and improving control, therapists help you move confidently, avoid future injuries, and build lasting strength. This is especially important for people recovering from nerve problems, injuries, or age-related balance issues.